 You’ve probably heard a lot about CBD oil lately. It’s revolutionizing the world of pain and anxiety management, and that’s fantastic! But do you know the difference between isolated CBD oil and Full Spectrum Hemp Oil? We are going to break it down for you and explain how you can guarantee you are actually getting what you pay for.
You’ve probably heard a lot about CBD oil lately. It’s revolutionizing the world of pain and anxiety management, and that’s fantastic! But do you know the difference between isolated CBD oil and Full Spectrum Hemp Oil? We are going to break it down for you and explain how you can guarantee you are actually getting what you pay for.
Benefits of Full Spectrum Hemp Oil
While both oils are derived from the Cannabis Sativa plant, Full Spectrum Hemp Oil (FSHO) contains CBD in addition to other natural plant compounds. These plant compounds are cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids. These compounds have the ability to integrate into our bodies’ own neurological and systemic pathways for positive health benefits. Studies have shown benefits include brain health, heart health, pain relief, muscle tension, anxiety, and skin health. The oil can be taken as a daily supplement to support homeostasis, or biological harmony, in our bodies. These oils aren’t regulated by the FDA, but there are ways to make sure you’re getting the real deal.
So what is the difference between cannabis and hemp?
Although viewed and treated differently, cannabis and hemp are, scientifically speaking, the same plant. They share the same genus, Cannabis, and the same species, Sativa. The difference is how the cannabis is bred and used, resulting in either a high concentration of THC (delta 9 Tetrahydrocannabinol) or CBD (cannabidiol). THC is only produced in the female plant, but some female plants can still be hemp plants if the THC level is low enough.
Chemically speaking, the difference is in which cannabinoid is predominant. A cannabis sativa plant that is CBD dominant, as opposed to THC dominant, is a hemp plant. Hemp plants contain no more than 0.3% (by dry weight) of THC, the psychoactive substance found in marijuana. By comparison, marijuana typically contains 5-20% THC.
You can’t get high on hemp.
What is the difference between THC and CBD?
Both THC and CBD have the exact same molecular structure: 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms. A slight difference in atom arrangement results in differing effects they have on your body.Both THC and CBD have the exact same molecular structure: 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms. A slight difference in atom arrangement results in differing effects they have on your body.
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the chemical responsible for most of marijuana’s psychological effects. THC affects a person’s memory, pleasure, movements, thinking, concentration, coordination, and sensory and time perception, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA).
CBD is a non-psychoactive compound. That means it doesn’t produce the “high” associated with THC. THC binds with the cannabinoid 1 (CB1) receptors in the brain, producing the high or sense of euphoria. CBD, on the other hand, binds very weakly, if at all, to CB1 receptors. In fact, it can interfere with the binding of THC and lessen the psychoactive effects.
CBD can increase the amount of anandamide in the body, known as the “bliss molecule.” Anandamide, synthesized in the brain, plays a role in the neural generation of pleasure and motivation. By stimulating the endocannabinoid system, CBD promotes homeostasis, reduces pain sensation, and decreases inflammation.
CBD has been used to help with the following symptoms:
- Seizures
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Pain
- Inflammation
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Migraines
What are cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are naturally occurring compounds found in the Cannabis sativa plant. There are more than 100 varieties of cannabinoids. These compounds, or chemicals, are produced throughout nature. THC and CBD are the most common cannabinoids. Plant cannabinoids all share a similar architecture, but each variation has a slightly different effect on our neurochemistry and other systems within our bodies.
The human body produces cannabis-like molecules we call endocannabinoids, or endogenous cannabinoids. Humans also produce endocannabinoid receptors. These receptors are in the central nervous system, with CB1 and CB2 being the two main types. They are also found throughout the entire body, including in the skin, immune cells, bone, fat tissue, liver, pancreas, skeletal muscle, heart, blood vessels, kidneys, and the gastrointestinal tract.The human endocannabinoid system encompasses a variety of functions, such as pain, memory, mood, appetite, stress, sleep, metabolism, immune function, and reproductive function. The main function of the endocannabinoid system is to maintain bodily homeostasis, or biological harmony.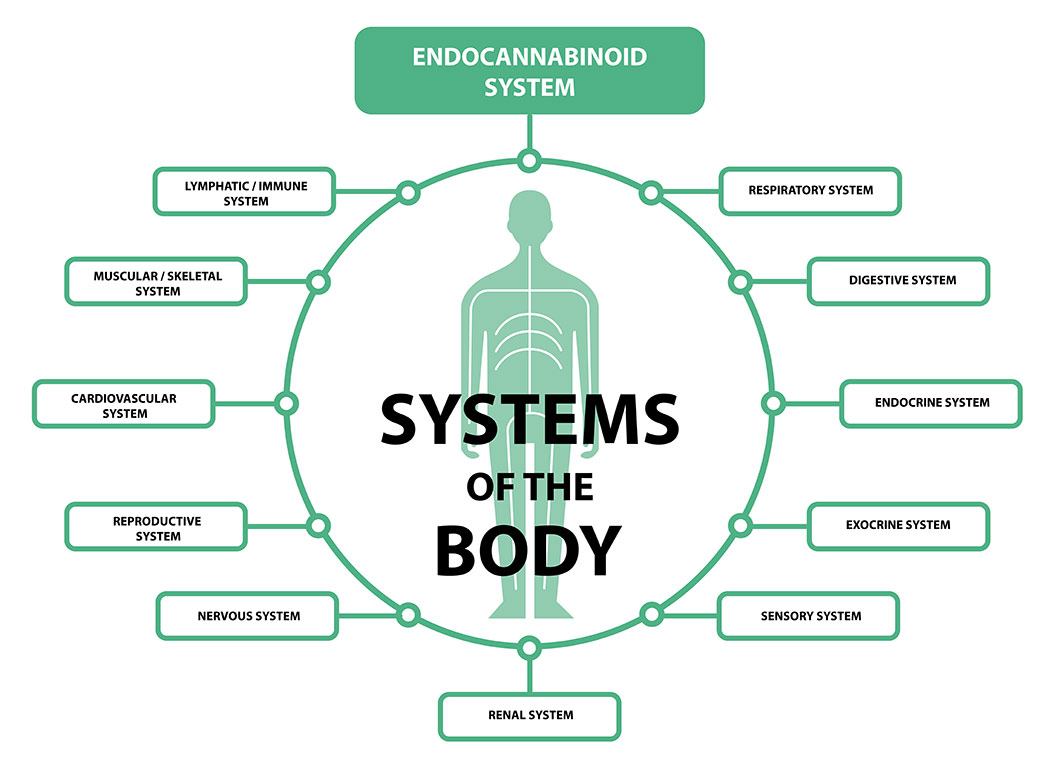
Plant cannabinoids can bind with the endocannabinoid receptors in our body, affecting the release of neurotransmitters in the brain. Neurotransmitters are chemicals responsible for relaying messages between cells. They also have roles in pain, memory, mood, appetite, stress, sleep, metabolism, immune function, and reproductive function.
What are Terpenes?
Terpenes are in the essential oils of the cannabis plant. They have a strong odor, giving cannabis products a unique taste and aroma. The resin glands of the plant produce terpenes along with cannabinoids.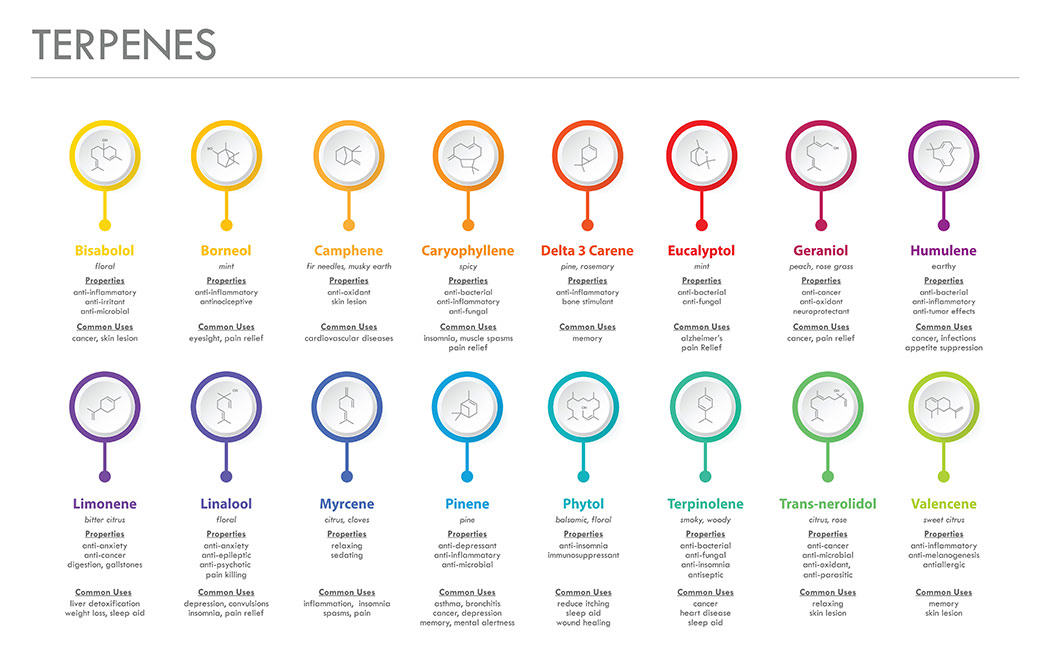 Some terpenes promote relaxation and stress relief, while others enhance focus and perception. The effects also include anti-inflammatory, analgesic, sedative, antifungal, anxiolytic, antioxidant, antimicrobial, antibiotic, appetite suppressant, sleep aid, antimutagenic, and immune boosting properties.
Some terpenes promote relaxation and stress relief, while others enhance focus and perception. The effects also include anti-inflammatory, analgesic, sedative, antifungal, anxiolytic, antioxidant, antimicrobial, antibiotic, appetite suppressant, sleep aid, antimutagenic, and immune boosting properties.
There are around 140 terpenes in the cannabis plant. Fruits, vegetables, flowers, and conifers also produce terpenes.
Common terpene strains found in full spectrum hemp oil include pinene, myrcene, limonene, linalool, and caryophyllene.
*See the chart above for benefits of these terpenes.*
What are Flavonoids?
Flavonoids are a group of plant metabolites that are part of the polyphenol class of phytonutrients primarily in edible plants, including hemp. They are responsible for the vivid colors in fruits and vegetables, such as citrus fruit, berries, and peppers. Well known for their antioxidant effects and anti-inflammatory health benefits, flavonoids also aid in longevity, weight management, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer prevention, and neurodegenerative disease prevention.
The following are the most common flavonoids in hemp:
- Kaempferol – reduces risk of chronic disease, especially cancer
- Luteolin – hypertension, inflammatory disorders, and cancer prevention
- Quercetin – arthritis, diabetes, heart and blood vessel health, cancer prevention
In addition, hemp contains unique flavonoids called cannflavins, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
So what’s the bottom line? Why choose full spectrum hemp oil over isolated CBD oil?
Full spectrum hemp oil has many health benefits in addition to CBD. Removing one single molecule from the full spectrum of a plant’s bioactive molecules can significantly limit the effects. If you want the combined powers of all the cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids, make sure to choose a full spectrum hemp oil.
If it’s not FDA approved, who regulates it?
To guarantee you are getting what you pay for, make sure your product comes with a Certificate of Analysis. This document from an accredited laboratory shows the quantity of various cannabinoids in a product. Manufacturers should send every batch of every product they make to a lab for testing to protect their customers and prove that their products have as much CBD as they advertise.
Unlike drug products approved by the FDA, unapproved CBD drug products have not been subject to FDA review as part of the drug approval process. There has been no FDA evaluation regarding whether they are safe and effective to treat a particular disease, what the proper dosage is, how they could interact with other drugs or foods, or whether they have dangerous side effects or other safety concerns.
The FDA is currently evaluating the regulatory frameworks that apply to certain cannabis-derived products intended for non-drug uses, including whether and/or how the FDA might consider updating its regulations, as well as whether potential legislation might be appropriate. At this time, military personnel are forbidden from using Hemp products or CBD oils.
References:
-
Medical News Today. Hemp oil benefits list.
-
Healthline. CBD vs. THC: Side effects.
-
Kight on Cannabis. What is the Difference Between Cannabis and Hemp?
-
News-Medical. What are Cannabinoids?
-
UCLA Health. Human Endocannabinoid System.
-
CBD Oil Review. How Does CBD Affect the Endocannabinoid System?
-
Pub Med. The role of the endocannabinoid system in the regulation of endocrine function and in the control of energy balance in humans.
-
News-Medical. What are Flavonoids?
-
Live Science. What Are Flavonoids?
-
US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health. A review of the dietary flavonoid, kaempferol on human health and cancer chemoprevention.
-
Science Direct. Luteolin.
-
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. What You Need to Know (And What We’re Working to Find Out) About Products Containing Cannabis or Cannabis-derived Compounds, Including CBD.
